Evaluate risks and benefits, as well as the social and ethical issues concerning the use of stem cells from embryos in medical research. Scientists have found somatic stem cells in more tissues than was once imagined, including the brain, skeletal muscle, skin, teeth, heart, gut, liver, ovarian cells, and testis.
Should Human Stem Cells Be Used To Make Partly Human
Interstitial cells in cnidarians, neoblast cells in planarians, and haemoblast stem cells in ascidians (urochordata).

Where are stem cells found in animals. By genetically marking stem cells, it is possible to show that nearly all cells of a mature plant descend from small groups of stem cells located in their growing apices. In mammals, they include, among others, hematopoietic stem cells, which replenish blood and immune cells, basal cells, which maintain the skin epithelium, and mesenchymal stem cells, which maintain bone, cartilage, muscle and fat cells. Discovered centuries ago, regeneration is a fascinating biological phenomenon that continues to intrigue.
Multipotent stem cells include many cell types traditionally classified as adult stem cells, including hematopoietic, mesenchymal, and neural stem cells. Also known as somatic stem cells (from greek σωματικóς, meaning of the body ), they can be found in juvenile, adult animals, and humans, unlike embryonic stem cells. They occur in most of the tissues in the body such as bone marrow and brain.
Stem cells are the sites of production of specialised cells in animals and have the potential to become different types of cell. There are two types of stem cell: Cord blood stem cells were discovered in 1978, and after the first cord blood transplant in 1988, the cord blood banking industry was formed.
Stem cells are involved in growth and repair. Stem cells are cells in animals that can continuously undergo cell division. Moreover, they are found in skeletal muscle, liver, pancreas, brain, eye, dental pulp, skin, bone marrow, blood and the lining of the gastrointestinal tract.
Pet stem cell therapy uses stem cells from the bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or fat of either your pet (known as autologous stem cell therapy) or another animal of the same species (known as allogeneic stem cell therapy). Commonly, the modifiers, “embryonic,” and “adult” are used to distinguish stem cells by the developmental stage of the animal from which they come, but these terms are becoming insufficient as new research has discovered how to turn fully differentiated adult cells back into embryonic stem cells and, conversely, adult stem cells, more. Stem cells in animal models of regeneration.
Furthermore, whereas animal stem cells are in general responsible for maintaining a specific tissue, plant stem cells generate complete organs, and as such resemble animal pluripotent embryonic stem (es) cells. Describe how stem cells could be used to help treat some medical conditions. They are vastly outnumbered by the progenitor cells and terminally differentiated cells that they.
These cells have the potential to regenerate all the cells and tissues that have been lost because of any kind of injury or disease. Adult stem cells are found in a tissue or organ and can differentiate to yield the specialized cell types of that tissue or organ. Found in the patient’s own blood and bone marrow, these stem cells can differentiate into the building blocks of blood, and may be an important consideration in treating immune, blood and circulatory disorders, without the compatibility problems associated with cord blood.
Researchers have discovered stem cells in amniotic fluid as well as umbilical cord blood. Also known by a tongue twister name, hematopoietic stem cells. An embryo develops from a fertilised egg.
Embryonic stem cells embryonic stem cells are controversial since they are derived from human embryos that have either been destroyed or harvested for science. Gurley,, alejandro sánchez alvarado, department of neurobiology and anatomy, howard hughes medical institute, university of utah, salt lake city, ut, 84132. The second to youngest stem cells are still called adult stem cells even though they can be collected at the time of delivery.
Cord tissue stem cells were discovered in the late '90s, and this discovery spurred cord tissue banking for. They are found in the blastocyst stage. A veterinarian injects the stem cells into the diseased area, such as a knee joint damaged by osteoarthritis.
Amniotic fluid fills the sac that surrounds and protects a developing fetus in the uterus. Embryonic pluripotent stem cells originate from totipotent cells in the fertilized egg. These cells can develop any type of cell and tissue in the body.
Adult stem cells are undifferentiated cells, found throughout the body after development, that multiply by cell division to replenish dying cells and regenerate damaged tissues. Cells at the early stages in the development of the embryo are stem cells. Describe in simple terms how cells genetically identical to a patient could be obtained.
Animal stem cells are the cells that produce new cells for the regeneration and repair of the existing tissues. Describe where stem cells can be found in animals and plants. Adult stem cells are a small minority of cells;
These stem cells also have the ability to change into specialized cells. The progeny of shoot stem cells form all the aboveground tissues, which indicates stem cell multipotency. Multipotent stem cells exhibit a variety of different types of morphologies that in many cases can be readily distinguished from one another, but are not necessarily uniquely identifiable from other types of differentiated cells.
Stem cells involved in agametic cloning in invertebrate taxa are of different kinds: Adult stem cells are a diverse stem cell population that can be found in many adult tissues, including, but not limited to, the blood, 106 bone marrow, 107 brain, 108 skin, 109 fat, 110 lung, 111 intestine, 112 and urethra 113 (fig.
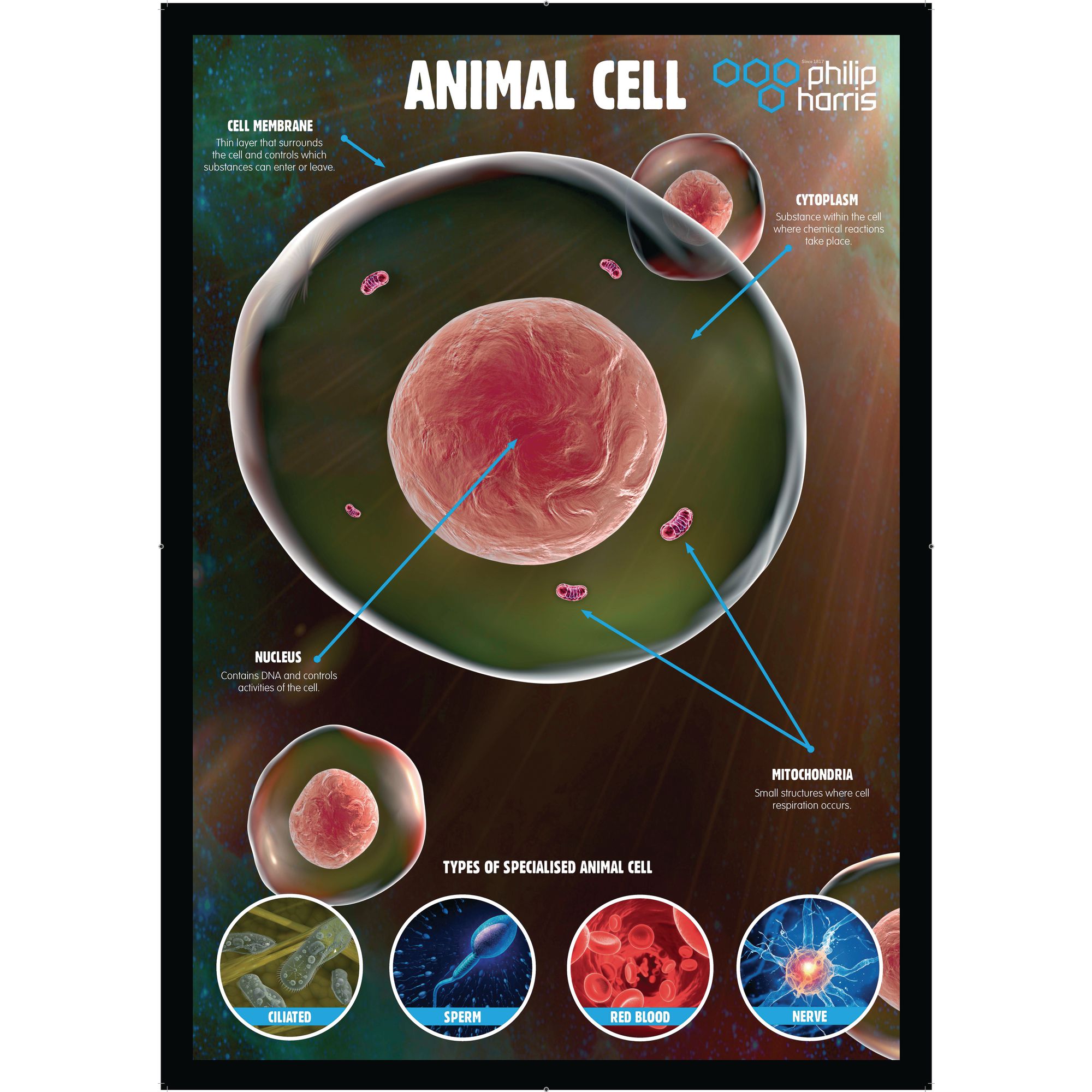
Animal Cells Poster E8R06633 Findel International
The Hemlock Tea Room and Ladies' Emporium HUMANANIMAL
What Is Cell Differentiation? The Student Room

Human or animal cells on blue background. Concept Early
/https://www.thestar.com/content/dam/thestar/life/health_wellness/2009/02/02/growing_human_dna_in_animal_embryos_may_not_create_prized_stem_cells_poses_risks_critics/stemcell.jpeg)
Growing human DNA in animal embryos may not create prized
Solve Israel's Problems » Please Share Our Articles

Concise Review Human‐Animal Neurological Chimeras
Stem Cell Cornerstone Animal Hospital

Generation of transgenic animals using spermatogonial stem

Primordial germ cellmediated transgenesis and genome

Plant and animal stem cells behave similarly, research
Stem Cell Therapy for Dogs Veterinary Hospital Clemmons

Figure 1 from Stem Cells for Cartilage Repair Preclinical

Global Animal Stem Cell Therapy Revenue Is Nearly 16.3 M

Fetal Stem Cells in Farm Animals Applications in Health

Schematic depiction of production of mice using iPS cells

