Trainers typically use a continuous. In the experiments, each time the animal pressed a lever or a bar, it received food or water as reinforcement 4.

The ABC's of Operant Conditioning Dog Training
Operant conditioning examples listed below and operant conditioning involving animal husbandry and her teeth of an example:
Operant conditioning examples in animals. If you want to train a simple stimulus/response, then the latter approach is most effective. The animal could be rewarded (food pallet) and punished (unpleasant electric shocks) when it exhibited certain behaviours, such as pressing the lever for rats or pecking keys for pigeons. One day, a woodpecker finds a particular tree that offers an especially abundant supply of the bird's favorite bugs.
Operant conditioning is different to classical conditioning as described by pavlov in that a desirable behaviour is reinforced and an undesirable behaviour, punished. Skinner developed the skinner box or the operant chamber, which recorded the behaviour of an organism in a specific time frame. This type of conditioning does not involve any voluntary choices by the animal;
However, some animals show negligible wait time and a. Your dog bites your hand when you're playing a ball game together. This association is built upon the use of reinforcement and/or punishment to encourage or discourage behavior.
He had created a box that you could only escape from by pushing or stepping on a lever to open a door. Watchdogs have their ferocity reinforced. For example, as part of their life cycle, female monarch butterflies lay their eggs exclusively on milkweed plants.
Animals learn by the principles of operant conditioning every day. Under no circumstances should you hit or yell at your dog. By encouraging natural, desirable behaviours through different forms of reinforcement, operant conditioning provides educational entertainment to our visitors, enrichment to the animals and.
Routledge and went into play behavior modification. Operant conditioning, as a method of training captive animals, is a practice increasingly recognised by zoological collections as a valuable addition to standard husbandry. The goal is to reduce the frequency of a behavior.
For example, woodpeckers find insects to eat by pecking holes in trees with their beaks. A pause after each food delivery—also called wait time or latency—followed by responding at an accelerated rate until the next food delivery. Her infant oral medication administration,.
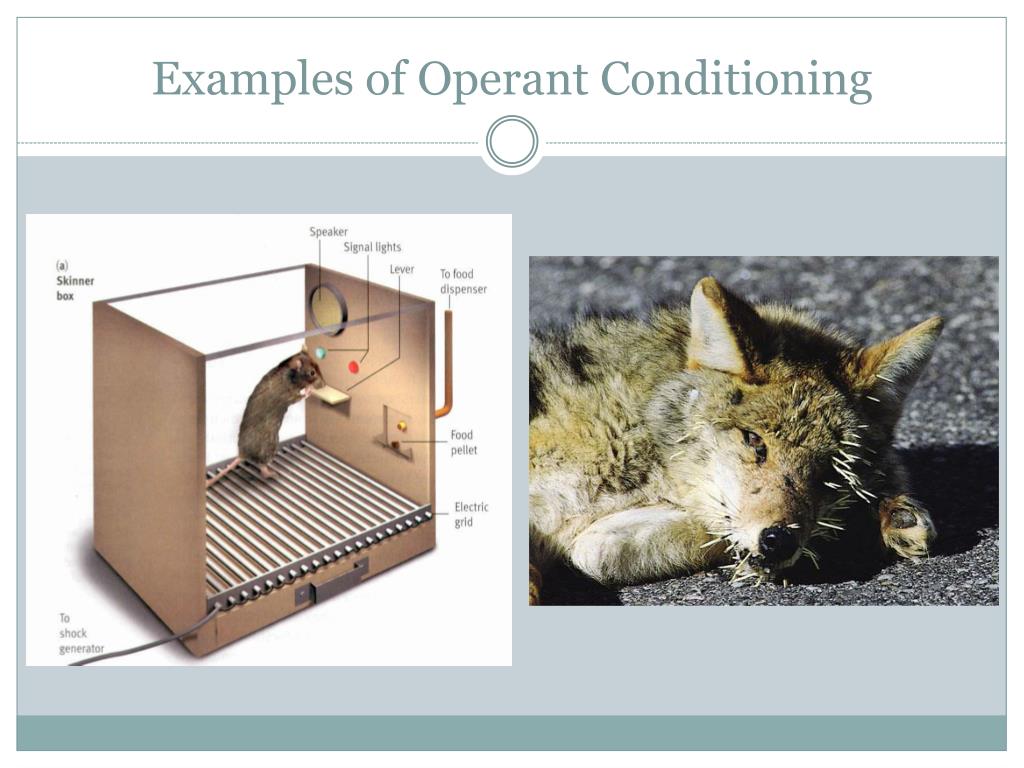
Operant conditioning in the wild. By encouraging behavior through positive reinforcement, trainers can effectively increase the. A skinner box, also known as an operant conditioning chamber, is a device used to objectively record an animal's behavior in a compressed time frame.
An american psychologist by the name of e.l thorndike is said to be one of the first to use a form of operant conditioning. The dallas zoo is a good example of a zoo in transition, from the old view that you should not interfere with the animals in any way, to an awareness of the clicker technology and its usefulness. A good example of the associative learning called operant conditioning in the wild is the interaction between monarch butterflies and certain birds, female monarch butterflies lay their eggs exclusively on milkweed plants.
Operant conditioning is the basic psychological tool used to train animals. An animal can be rewarded or punished for engaging in certain behaviors, such as lever pressing (for rats) or key pecking (for pigeons). The ferocity of the dog will increase as it associates the reward with the behavior and encourages it to increase the amount received.
Trainers implement these basic tactics to train the animals to perform various behaviors. The response or reaction is reflexive (e.g., blinking or salivating) and not dependent on operant learning. It is a highly specialised form of learning known as instrumental learning and is used in many contexts including good parenting and even training animals.
Rewarding a child for good behavior or punishing a child for bad behavior, slot. Sales workers are encouraged to sell. Many people train their pets with positive reinforcement.
Animals learn by the principles of operant conditioning every day. Operant and classical conditioning are two ways animals and humans learn. California zoo training experts tim desmond and gale laule, of active environments, inc., started an operant program with the dallas zoo elephants.
Animal instinct, learning, and emotions a good example of the associative learning called operant conditioning in the wild is the interaction between monarch butterflies and certain birds. Receiving a reward for acting in a certain way. For example, woodpeckers find insects to eat by pecking holes in trees with their beaks.
What is an example of operant conditioning in the wild. One day, a woodpecker finds a particular tree that offers an especially abundant supply of the bird's favorite bugs. If you’re going to build, change, or break a habit, then operant conditioning is the way to go.
Operant conditioning occurs when an association is made between a particular behavior and a consequence for that behavior. Through positive encouragement every time they attack a stranger or bite a thief. Punishment can consist of ending a game or taking a toy away from it;
To study operant conditioning, bf skinner made a chamber, called the skinner box, and put a small animal inside. Operant conditioning was first defined and studied by behavioral psychologist b.f. Positive reinforcement describes the best known examples of operant conditioning:
You end the game and leave it playing alone. Skinner, who conducted several well. Thorndike would put the cats in the box and monitor how long it took them to escape.
Through a system of rewards and bonuses. He used cats and a puzzle box.

Classical conditioning has important in

SmartPups Conditioning The Nitty Gritty of Clean

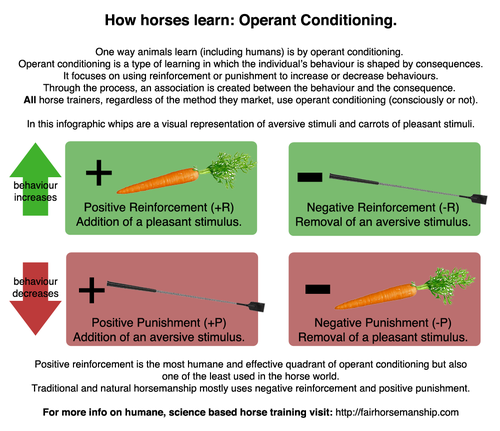
The Four (Emotional) Quadrants of Operant Conditioning

Operant and classical conditioning for highwelfare animal
/2794863-operant-conditioning-a21-5b242abe8e1b6e0036fafff6.png)
In Classical Conditioning Organisms Learn The Association

Reactive Dog Poster Bundle (Free Download or Donation

WHAT IS AVERSIVE TRAINING? And why you should stop using
/learning-study-guide-2795698_FINAL-5bec544ac9e77c005185519d.png)
🎉 Examples of classical conditioning on humans. Untitled

Pin by Maggie on Great stuff about Dogs! Operant
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2794863-operant-conditioning-a21-5b242abe8e1b6e0036fafff6.png)
What Is Operant Conditioning and How Does It Work?
Operant Conditioning, using positive vs. negative dog

Positive and negative reinforcement and punishment
About Us American Canine Academy

The Four Quadrants of Operant Conditioning Operant
PPT Animal Behavior PowerPoint Presentation, free
/OperantConditioning-5c00cf7ec9e77c00017f69c5.jpg)
What Is Operant Conditioning? Definition and Examples

Operant Conditioning Easy Science Operant conditioning

Operant Conditioning Operant conditioning, Classical

Operant conditioning Animals wild, Positive