Gas exchange in gills and lungs operates by this process. (the animal cell equivalent is called the gap junction.) the plasmodesmata consist of pores, or channels, lying between individual plant cells, and connect the symplastic space in the plant.
Model 2 Osmosis in Plant and Animal Cells
Once these signals are detected and received, the cell begins to move.
How do animal cells move. And even cells inside multicellular organisms may need to get around. The cytoplasm eventually tears away from the cell wall. Some simply float through water or other liquids.
This is when the cytoplasm shrinks due to the loss of water but the cell wall fails to shrink due to its tough structure. Unlike an animal cell, the plant cell does not burst. Moving across cell membranes by random motion.
Then you can have a brief description of each nutrient a mineral. This is because plant cells have a rigid cell wall around the plasma membrane. Each one of these cells can grow, reproduce, respond to changes in the environment, move, and metabolize food for fuel.
An animal cell can become crenated if too much water is lost ; Plant cells play an important part in supporting the plant. Upon swelling with water they become turgid.
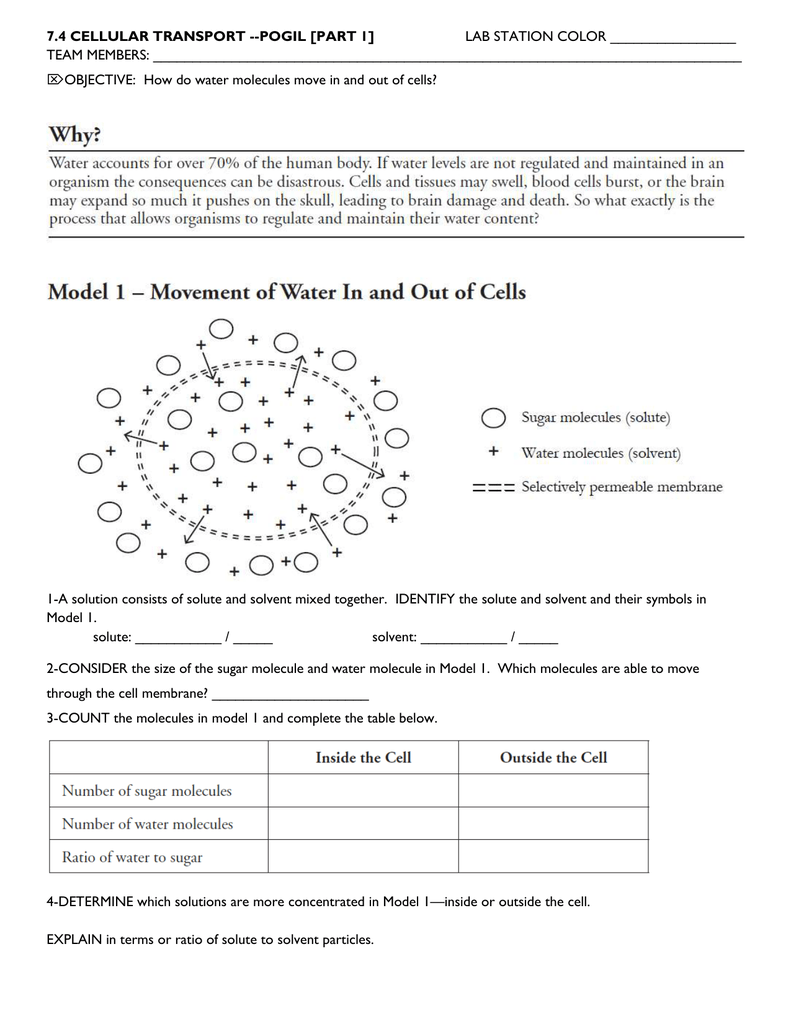
It is permeable to some substances but not to others and so controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. They can also be termed as bridges between two plant cells. Note that both plant and animal cells are surrounded by a selectively permeable membrane, and that plant cells are also surrounded by a permeable, rigid, outer cell wall.
Let's say for example say animals required different nutrients and minerals for proper functioning. In these cells, the pyruvate formed at the last step of stage 2 is rapidly transported into the mitochondria, where it is converted into co 2 plus acetyl coa, which is then completely oxidized to co 2 and h 2 o. One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane.
A plant cell can become plasmolysed if too much water is lost. Once these signals are detected and received, the cell begins to move. To do to make the cell function properly.
The cells that make up muscles contract and then relax back to original size. Animal cells do not have a cell wall. And sperm needs to “swim” to fertilize eggs.
Three types of muscle fibers occur in animals (the only taxonomic kingdom to have muscle cells): Tiny microscopic fibres in these cells compress by sliding in past each other like a sliding glass door being opened and then shut again. As food is often hard to get, we may reasonably expect animals to move in ways that minimise energy consumption.
So how does an animal cell work? Many types of cells can move. Cell movement is prompted by chemical or physical signals that are detected by proteins found on cell membranes.
After the description, you can say that absorbed nutrients are utilized by the cells to provide energy for growth, movement, and cell division and have an expounding discussion of the respiration process. Active transport is the movement of particles. Cost of animal movement, usually by measuring oxygen consumption.
Muscle tissue facilitates movement of the animal by contraction of individual muscle cells (referred to as muscle fibers ). They change size and shape when put into solutions that are at a different. Furthermore, these cells exhibit the presence of dna inside the nucleus.
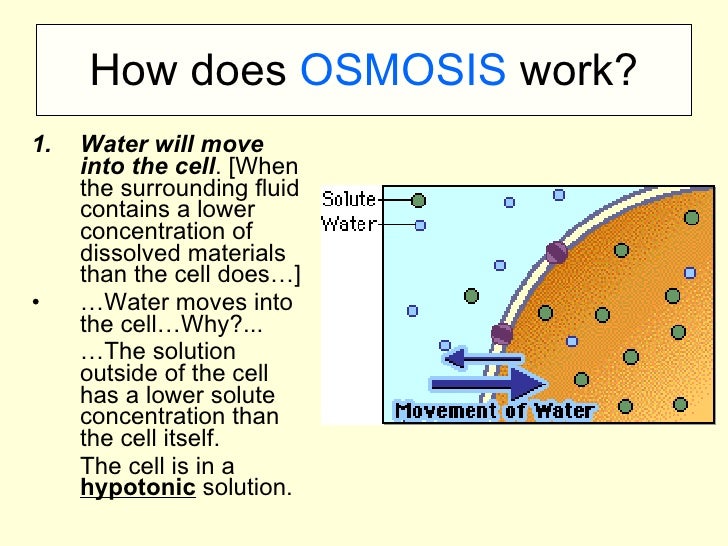
Cell structure function present in plant/animal cells cell wall protects and supports plant cells plant cells only centriole important in cell division animal cells only chloroplast site where photosynthesis occurs plant cells only cilia aids in moving the cell and moving substances along the surface of. How an animal cell works. The water moves from a region of low osmolarity (extracellular fluid) to a region of high osmolarity (inside the cell).
For most animal and plant cells, glycolysis is only a prelude to the third and final stage of the breakdown of food molecules. The relative amount of water movement into and out of the cells is indicated by the size of the arrows. Cells move in several ways.
For example, horses walk slowly, trot at current biology vol 15 no 16 r618 branches of mechanical engineering that have proved useful in the study of animal mechanics. For example, immune system cells must move toward invaders. To be able to move, the cell must attach itself to a surface and use its front to push to exert the force it needs.
The cell would then expand. Diffusion is one principle method of movement of substances within cells, as well as the method for essential small molecules to cross the cell membrane.

What Is An Animal? Today's Latest Economics & Business News

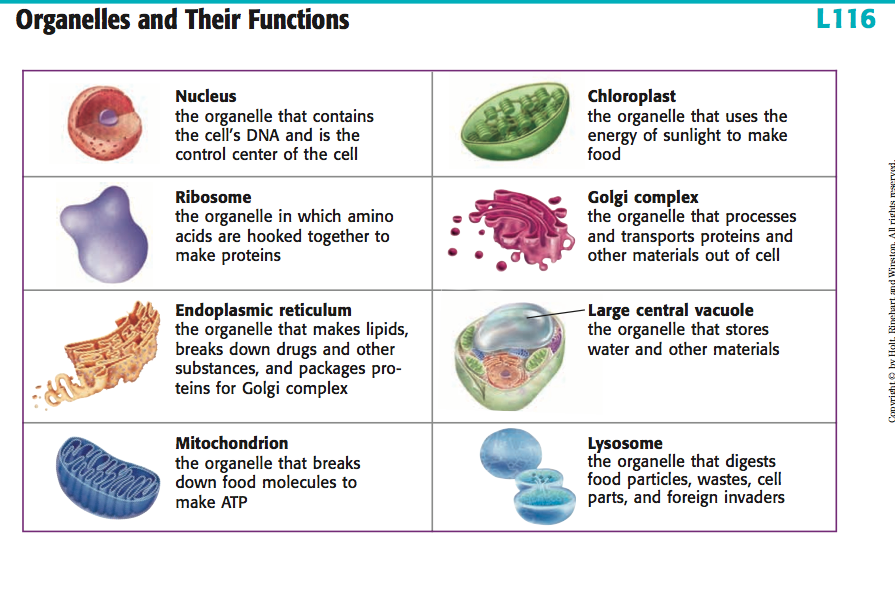
Animal Cell Organelles And Their Functions Escons

Saharart_609_12 ใบงานที่ 2 บทความสารคดี

30+ Why do animals not have chloroplasts ideas Animals 3d
What happens to animal cells kept in a Hypertonic solution

Molecular Expressions Cell Biology Animal Cell Structure

Zeal To Move Through Settlements Anew To Drive The Single
Cell Structure and Function Know what makes you live.
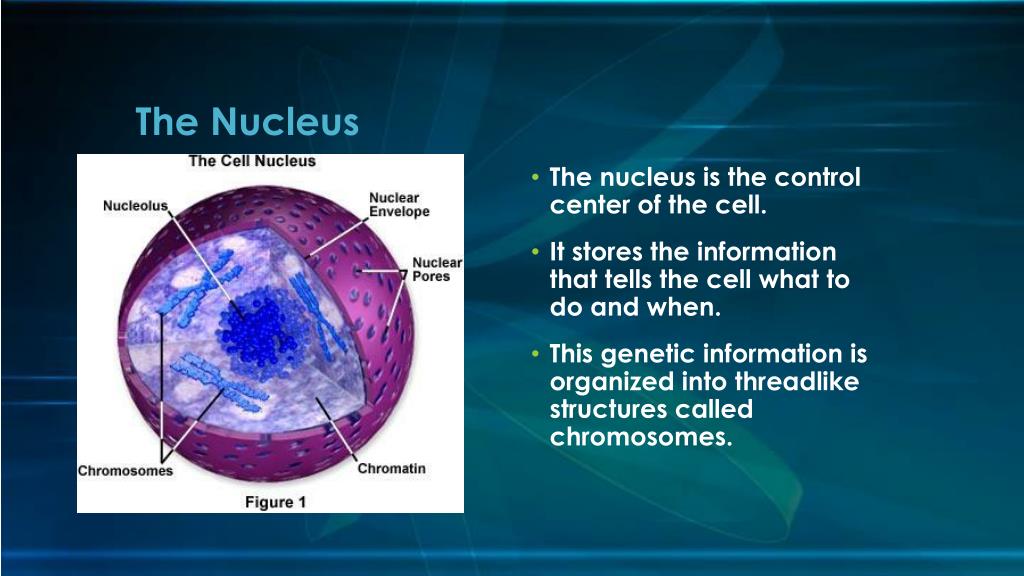
PPT Plant and Animal Cells PowerPoint Presentation, free

Biology Form 4 SMK USJ 13 NOTES Movement of Substances

Comparison of plant and animal cell

Animal Cell Organelles And Their Functions Escons
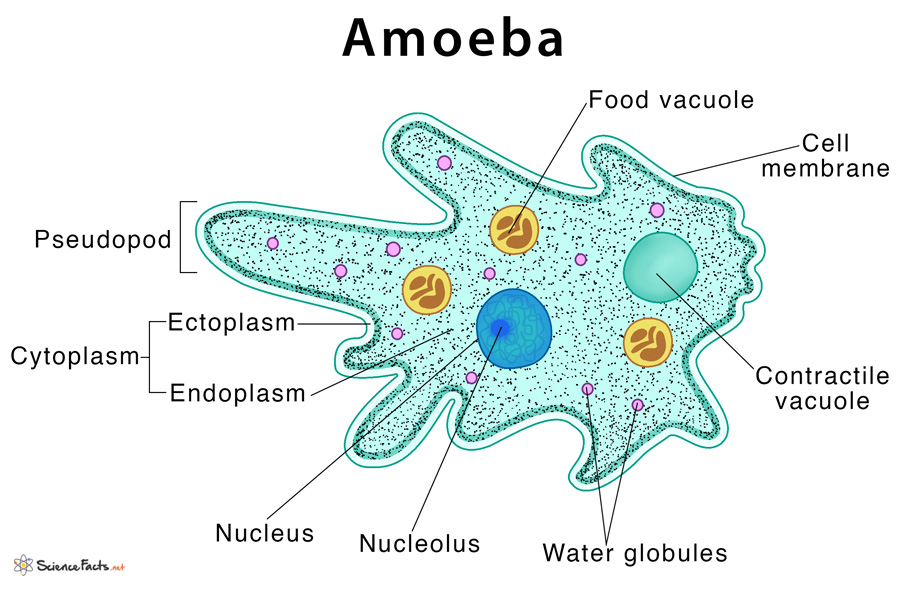
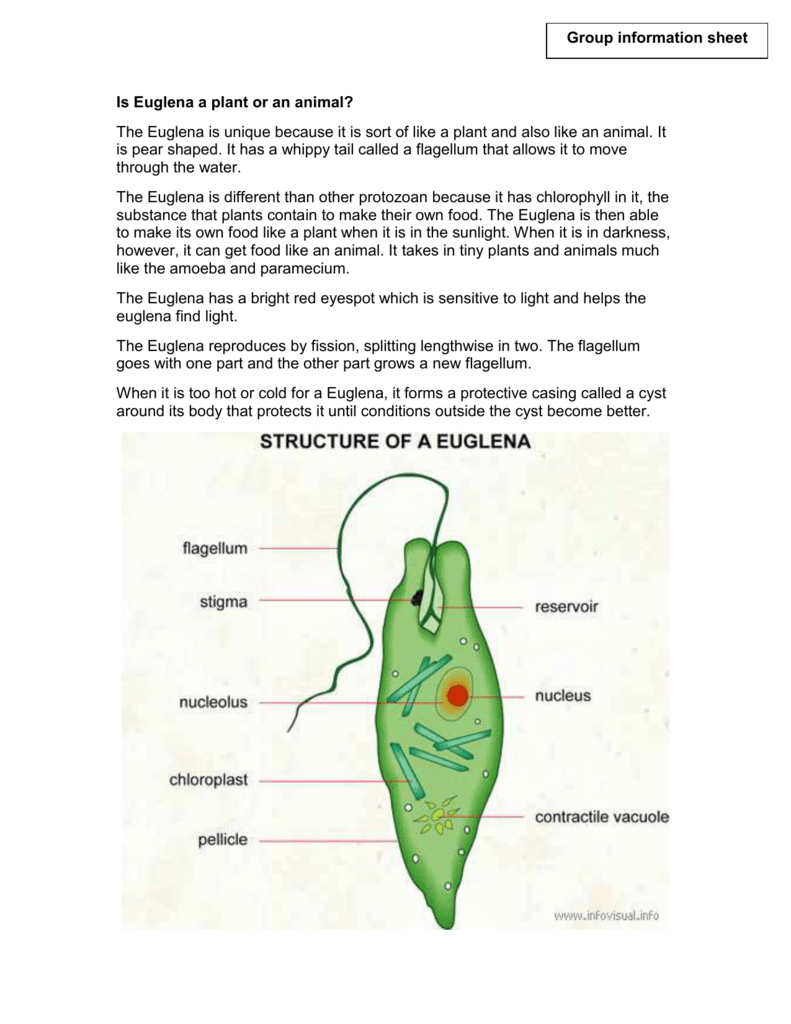
Amoeba Definition, Structure, & Characteristics with Diagram

Intercellular Connections Are Developmentally Controlled