Animals have been used to study the reinforcing mechanisms that promote or discourage certain behaviors. Lana the chimpanzee was able to learn a lot about human communication with the use of lexigrams.
Lexigrams are symbols that correspond to words or ideas.

Why do we study animals in psychology. In addition, animal research has illuminated the complicated interactions between addictive behavior and the environment. Their brains are larger than mice, and the animals are less timid and more intelligent. Ethology, or the study of animals in their natural habitats, sheds light on how animals interact with each other.
People matter a lot but they are complicated. Rats are often used to study behaviour in psychology experiments. When researchers study animal behaviour, they describe behaviour instead of inferring behaviour, in order to avoid anthropomorphism.
Although it is impossible to directly ask animals if they are happy or sad, we can study animal behaviour in order to gain insight about the subjective states (or feelings) of animals. As any pet owner knows, it’s tempting to project a human interpretation onto animal behaviour. Psychologists realize that the brains of experimental animals are not miniature human brains but only serve as a model for it, assuming that basic principles of brain organization are common across mammalian species (canadian council on animal care, 1993) moreover, psychology is concerned with understanding and controlling psychopathology, such as.
The study of animal behaviour provides a. Animals are good research subjects for a variety of reasons. In the 1950s research which used animal subjects to investigate early life experiences and the ability for organisms to form attachments contributed significantly to the field of developmental psychology.
Behavioural therapies are derived from animal research. Studies typically use animals when time requirements, risk, the need to control behavioral history, or other conditions make it impossible to use humans or when there are other practical or ethical reasons not to use humans. Beyond social psychology, animal studies have been of great importance in the increased understanding and development of treatments for neurological and psychological disorders.
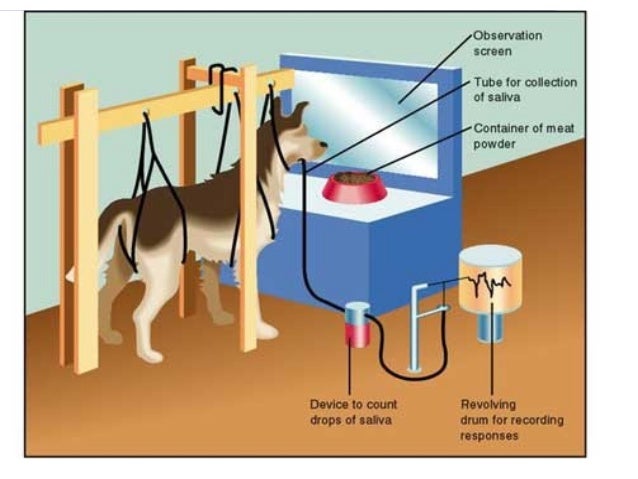
Although rats do not ‘think’ like humans, some of their brain structure resembles the more primitive elements of human brains, and hence they can be used to model some human behaviours. From pavlov’s dogs and skinner’s rats to more recent studies involving the language abilities of apes, animals feature heavily in all the main approaches, but especially the learning approach. The third answer to the question, why is zoology important to us is to understand the urgency of preserving the animals.
The underlying assumption is that to some degree the laws of behavior are the same for all species and that therefore knowledge gained by studying rats, dogs, cats and other animals can be generalised to humans. Animal behavior can often imitate our own. Chapter one why do we need evolution?
Some animal psychologists study animal behavior because they are deeply interested in animal rights. Studying zoology would help people achieve clarity over the common myths we have on different wild animals. This is a challenging field.
Some animals matter to us a lot. Scientists study animals when there is no alternative and it is impractical or unethical to study humans. Comparative psychology is the study of animals in order to find out about humans.
Why do you need to understand animal behaviour? Psychologists have long studied chimps and other animals with two principal, related aims: They were invented by duane rumbaugh.
The comparative method involves comparing the similarities and differences among species to gain an understanding of evolutionary relationships. To find out the capabilities of the animal mind, and to discover what makes us truly unique, if anything. Comparative psychology often utilizes a comparative method to study animal behavior.
The study of animal behavior is a cornerstone of psychology for several reasons. Animals have long played an important role as research animals in the field of science by human kind since ancient greeks, when aristotle used animals as a dissection. Gain an understanding of animal psychology so that you can work with animals more effectively or even manage undesirable pet behaviour better.
Studying this subject would help people know the real facts about animals. Psychologists and biologists study animal behavior for practical and philosophical reasons. You will gain an insight into why we to study animal behaviour, and how observations can help us yo understand how they live.
They are biologically similar to humans and susceptible to many of the same health problems. Scientists study dogs, cats, and farm animals to improve the ways we maintain them. The comparative method can also be used to compare modern species of animals to ancient species.
And many researchers also believe that studying animal behavior can help us develop a better understanding of human psychology. There is much to find out by looking at research on the linguistics of primates. The study of animal behaviour provides a foundation for animal training, or more generally, animal care.
Animals are used in research and experiments by scientists to advance human knowledge and find cures to diseases such as asthma. This course will also help you learn how to get reliable results from your observations, and the.

Psychology of Attraction 8 Weird Reasons Why People Fall

Animals feel pain. Why do people believe they don't? Big

Animal Research PowerPoint Animals and Morality

The Moral Animal Why We Are, the Way We Are The New

Is Animal Research Acceptable? Psychology Today

Why Scientists Should Use Magic to Study Animal Intelligence

Life in Keele Psychology. Hey! I’m Jack Medlin, and this

3 Ways to Study Psychology wikiHow

Introductory Psychology Research Design

Does AnimalAssisted Therapy Really Work? Psychology Today

Animals in Dreams Psychologist World

Scientific Principles in Psychology

Shaping in Psychology Behavior Modification Through the
Why We Love Animals So Much Anthropology, Psychology

Pursuing a Career in Experimental Psychology

Animal Psychology Advanced Diploma Employee CPD

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-four-major-goals-of-psychology-2795603_color1-5b76d1944cedfd0025b35c6c.png)