Histology is the study of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of animals and plants. They don't eat other plants, but animals eat the food plants make which is stored in different parts of plants.
Main differences between Plant cell and Animal cell QS Study
Digestive system (growth) circulatory system brain (avoid danger) muscles external structures:
Study of structure of plants and animals. Evs project on study of birds,insects and plants. A structure is anything made up of parts held together. Like animals, plants have internal and external structures that serve different functions for survival, growth, and reproduction.
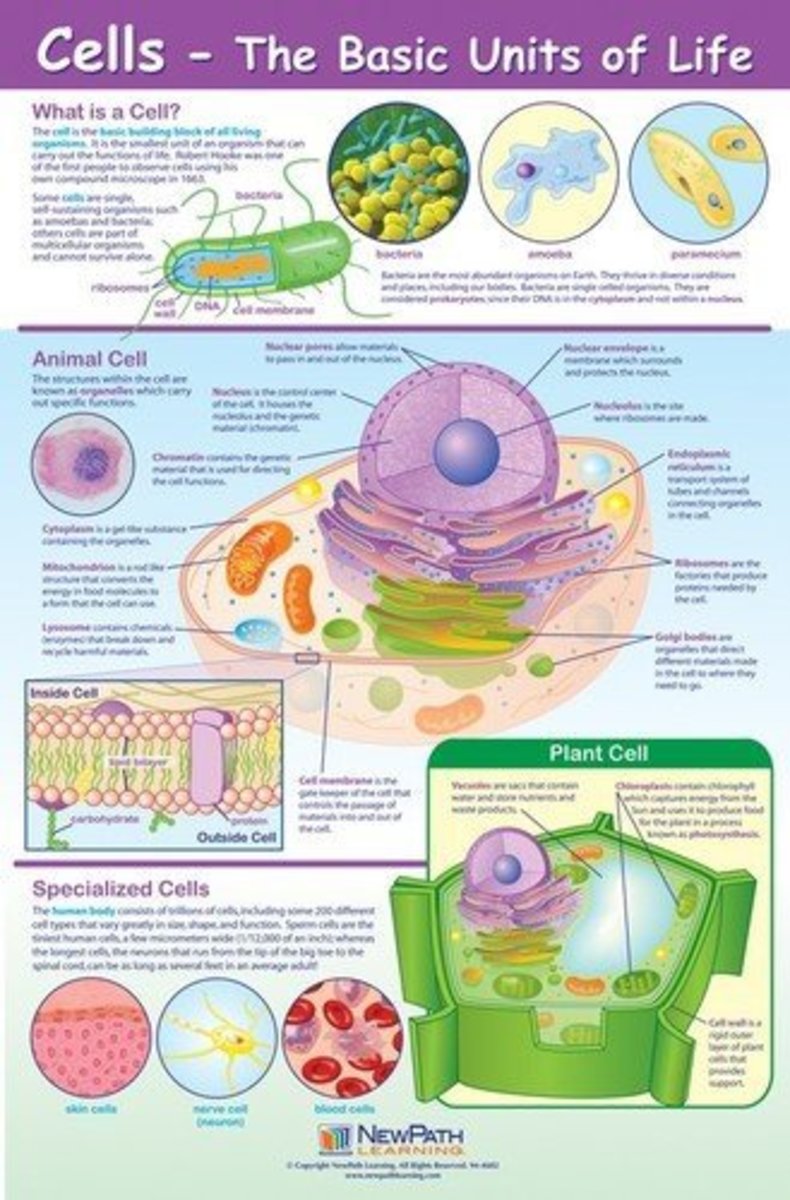
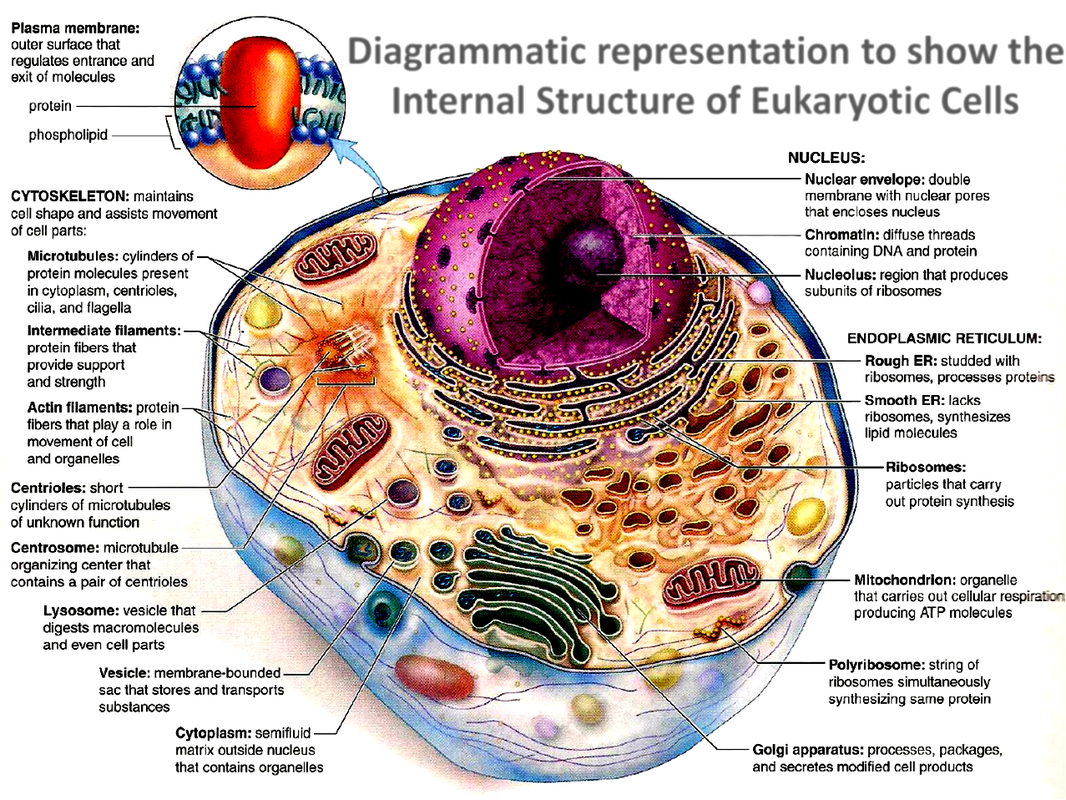
Structure of plant and animal cell it is important to know the component of cell i.e plasma membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes, golgi bodies, mitochondria, lysosomes, and plastids etc. Plants and animals have many structures that help them survive. They can incidentally be introduced to the concept that plants make their own food;
Chemical ecology the study of how plants and animals use chemicals and chemical signals in their interactions with each other and their environment. Other structures are external, like skin, eyes, and claws. In this unit of study, students develop an understanding that plants and animals have internal and external structures that function to support survival, growth, behavior, and reproduction.
Exploring edible cactus day 4 handson learning(the this usually happens on a large scale. The term anatomy also refers to the study of biological structure but usually suggests study of the. The study of plants is called botany, the person who studies plants is called a botanist.
Botany is a field of life sciences which. After reading the various chapters of structural organization in animals and plants, you will be able to understand various parts of the flowering plants, the internal structure of plant body and the various tissues along with their functions in the animal system. Morphology is a branch of zoology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features.
Morphology, in biology, the study of the size, shape, and structure of animals, plants, and microorganisms and of the relationships of their constituent parts. The crosscutting concepts of systems and system models are called out as organizing concepts for this disciplinary core idea. Gross anatomy is the study of structures large enough to be seen with the naked eye, and also includes superficial anatomy or surface anatomy, the study by sight of the external body features.
These structures of animals and plants under study show homology, i.e. Mcqs on structural organization in plants and animals. Agriculture is the science of producing plants and livestock from the natural resources of the earth.
The cellular composition may be different, but cells form the basis of life. Air, water, food legs tail how does the plant or animal support survival, growth, behavior, and reproduction? The leaves gather energy from the sun and protect the plant against water loss and fungal or bacterial attacks.
Z oology is the study of animal kingdom which includes the anatomy, physiology, evolution,. Chemistry the field of science that deals with the composition, structure and properties of substances and how they interact with. Leaves are the site of photosynthesis a key life process in plants.
Some structures are internal, like the lungs, brain, or heart. Microscopic anatomy is the study of structures on a microscopic scale, along with histology (the study of tissues), and embryology (the study of an organism in its immature condition). Learners need to identify different basic structures (parts) in plants.
Scientists who work in this field are called chemical ecologists. So, cytology simply means the study of the structure and function of plant and animal cells. In other words, the basic constituency of life form on earth is a cell.
• roots anchor the plant and take in water and nutrients from the soil. There is also a comparative discussion of earthworm, cockroach and frog. Structural organization in animals or any other life form for that matter at the fundamental level remains the same.
3) in case of animals. The term refers to the general aspects of biological form and arrangement of the parts of a plant or an animal. Internal and external structures of plants and animals i chose:
The structures depict the wings of a bat and wings of an insect (see fig. Some structures are unique, like the long neck of. Similarity in the fundamental (basic) structures due to shared or common embryonic origin but all of these organs/features performs different functions.
Study of animals and plants. Developmental biology is the study of the processes by which animals and plants reproduce and grow. • the stem provides support and.
They need to explore visible differences between different plants. The discipline includes the study of embryonic development , cellular differentiation , regeneration , asexual and sexual reproduction , metamorphosis , and the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism.

kate on Instagram “animal 🦋 + plant 🌿 cell illustrations
Study of the Structure of Plant and Animal Cells
Label the Plant and Animal Cells (Color)

Mrs. Paul Biology Biology Notes/Charts 20152016

2 NEW DOWNLOADS Plant & Animal Cell Posters (Labeled

UNIT ONE Cell and Cell Division AICE Biology Cambridge

Study the diagram of a cell. Which structures are found in

Cell Parts and Functions Study Guide Plant cell project

Animal cell v/s Plant cells Regeneration biology

Biology college, Teaching biology, Science cells

study the diagram of a cell which structures are found in

SPIRITUALISM THE KEY TO HUMAN NATURE Cell structure

Animal and Plant Cells + Organelles Read and Apply {NGSS
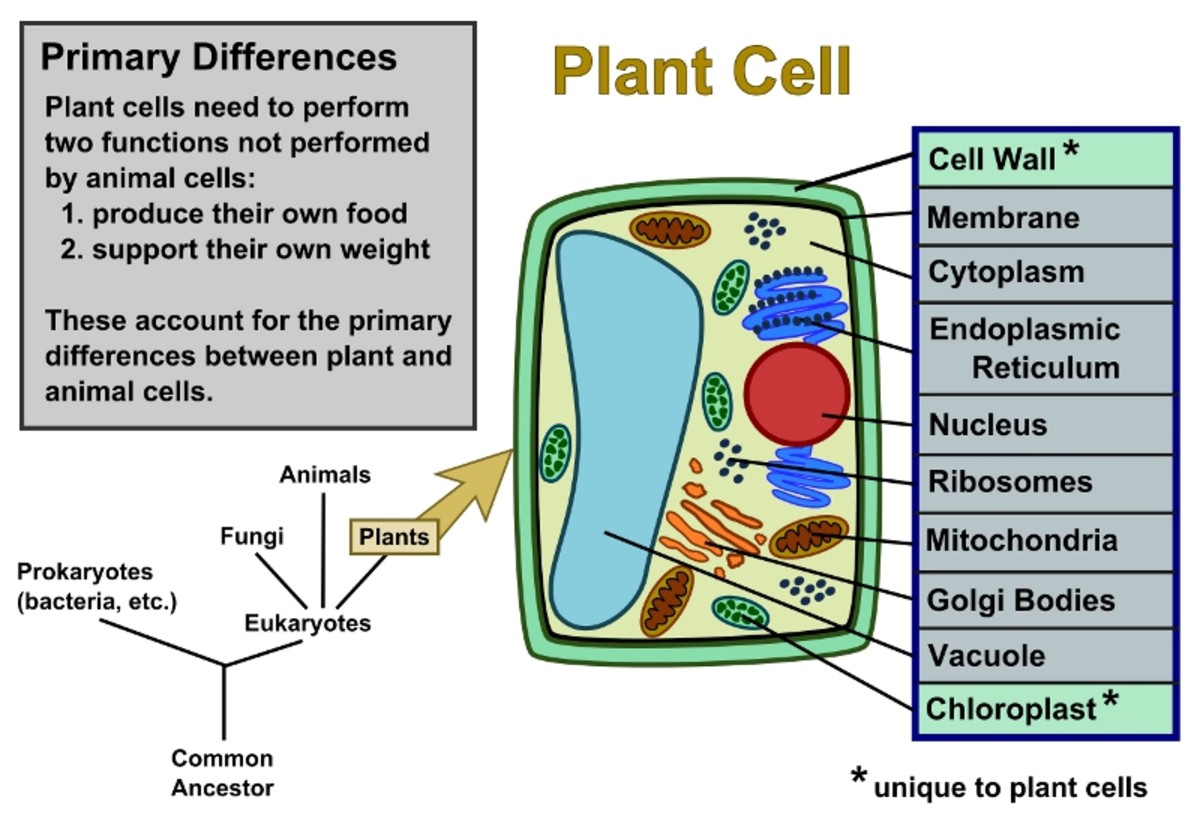
Write differences between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Mrs. Paul Biology Biology Notes/Charts 20152016

Animal and Plant Homeostasis and Physiology Study Guides

Us The Study of Life Biology Exploring Science